RabbitMQ 在互联网架构中发挥了很重要的作用,更是在大型业务系统实施中扮演了很重要的角色。
概念说明
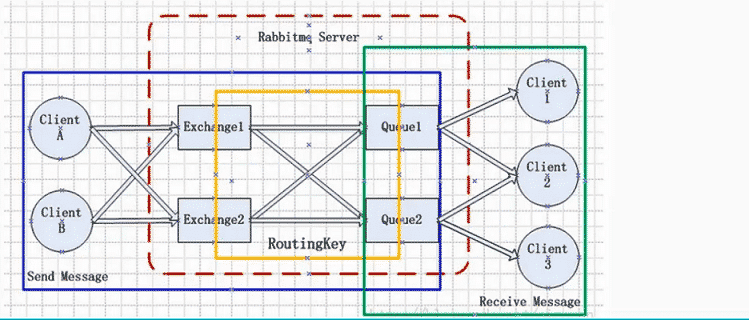
整体组成
- Broker:简单来说就是消息队列服务器实体。
- Exchange:消息交换机,它指定消息按什么规则,路由到哪个队列。
- Queue:消息队列载体,每个消息都会被投入到一个或多个队列。
- Binding:绑定,它的作用就是把 exchange 和 queue 按照路由规则绑定起来。
- Routing Key:路由关键字,exchange 根据这个关键字把消息路由投递给 queue。
- vhost:虚拟主机,一个broker里可以开设多个vhost,用作不同用户的权限分离。
- producer:消息生产者,就是投递消息的程序。
- consumer:消息消费者,就是接受消息的程序。
- channel:消息通道,在客户端的每个连接里,可建立多个 channel,每个 channel 代表一个会话任务。
Bindings are rules that exchanges use to route messages to queues. Bindings may have an optional routing key attribute used by some exchange types. The purpose of the routing key is to select certain messages published to an exchange to be routed to the bound queue. In other words, the routing key acts like a filter.
Exchange
Exchange 接收消息并将消息路由给 Queue,其重要属性包括:
- Name
- Durability (exchanges survive broker restart)
- Auto-delete (exchange is deleted when last queue is unbound from it)
- Arguments (optional, used by plugins and broker-specific features)
RabbitMQ 共支持 fanout、direct、topic、header 这几种类型的 Exchange:
| 类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| fanout | 将消息广播给绑定的队列,忽略对应的 routing key |
| direct | 将消息中的 RoutingKey 与该 Exchange 关联的所有 Binding 中的 RoutingKey Key 进行比较,如果相等,则发送到该 Binding 对应的 Queue 中 |
| topic | 照正则表达式,对 Routing Key 与 Binding Key 进行匹配,如果匹配成功,则发送到对应的 Queue 中 |
| header | 忽略 routing key,按照消息头里的属性参数进行,使用较少不再详细记录 |
需要注意的是,当新建 queue 时若不指定 exchange,则这个 queue 使用系统的默认交换机(类型为 direct) default exchange 上,对应的 routing key 就是队列名字。默认交换机强制绑定到所有队列。如下:
The default exchange is implicitly bound to every queue, with a routing key equal to the queue name. It is not possible to explicitly bind to, or unbind from the default exchange. It also cannot be deleted.
Queue
重要属性包括:
- Name(队列名不允许以 amq 开头)
- Durable (the queue will survive a broker restart)
- Exclusive (used by only one connection and the queue will be deleted when that connection closes)
- Auto-delete (queue that has had at least one consumer is deleted when last consumer unsubscribes)
- Arguments (optional; used by plugins and broker-specific features such as message TTL, queue length limit, etc)
当创建一个已存在的队列时,若指定的队列参数与现有队列参数不一致则会返回 406 错误;若参数一致则返回成功,不会对现有队列做任何调整。
消息发送流程
消息队列的使用过程大概如下:
- 1)客户端连接到消息队列服务器,打开一个 Channel。
- 2)客户端声明一个 Exchange,并设置相关属性。
- 3)客户端声明一个 queue,并设置相关属性。
- 4)客户端使用 routing key,在 exchange 和 queue 之间建立好绑定关系。
- 5)客户端投递消息到Exchange
Exchange 接收到消息后,就根据消息的 key 和已经设置的 binding,进行消息路由,将消息投递到一个或多个队列里。
If AMQP message cannot be routed to any queue (for example, because there are no bindings for the exchange it was published to) it is either dropped or returned to the publisher, depending on message attributes the publisher has set.
若一条消息无法路由发送给任何一个队列,则这个消息会被丢弃或者回退给生产者,取决于生产者的设置。
消息持久化
RabbitMQ 支持消息的持久化,也就是数据写在磁盘上。消息队列持久化包括 3 个部分:
- 1)exchange 持久化,在声明时指定 durable = 1
- 2)queue 持久化,在声明时指定 durable = 1
- 3)消息持久化,在投递时指定 delivery_mode = 2(1 是非持久化)
如果 exchange 和 queue 都是持久化的,那么它们之间的 binding 也是持久化的;如果 exchange 和 queue 两者之间有一个持久化,一个非持久化,就不允许建立绑定。
消息确认机制
Broker 发出消息后,应该何时删除消息? AMQP 0-9-1 规范提供以下两种选择:
- [自动确认] 消息发送给消费者后 (using either
basic.deliverorbasic.get-okAMQP methods). - [显式确认] 消费者回馈确认后 (using
basic.ackAMQP method).
作用
异步处理、系统解耦、削峰填谷;
安装使用管理
安装
centos 7 下执行如下:
curl -s https://packagecloud.io/install/repositories/rabbitmq/erlang/script.rpm.sh | sudo bash
curl -s https://packagecloud.io/install/repositories/rabbitmq/rabbitmq-server/script.rpm.sh | sudo bash
yum install rabbitmq-server
systemctl status rabbitmq-server.service
systemctl start rabbitmq-server.service
systemctl status rabbitmq-server.service
基本管理
rabbitmqctl status
rabbitmqctl list_queues
rabbitmqctl list_queues [the queue name] messages_ready messages_unacknowledged
rabbitmqctl list_exchanges
rabbitmqctl list_bindings
用户权限管理
rabbitmqctl list_users
rabbitmqctl list_permissions
rabbitmqctl add_user <user> pwd
rabbitmqctl set_permissions <user> '.*' '.*' '.*' (<conf> <write> <read>,正则表达式,'.*'表示所有权限)
rabbitmqctl clear_permissions <user>
rabbitmqctl set_user_tags <user> [administrator | monitoring | policymaker | management]
参考
http://www.rabbitmq.com/management.htmlNote that since “administrator” does everything “monitoring” does, and “monitoring” does everything “management” does, you frequently only need to give each user a maximum of one tag.
Normal RabbitMQ permissions still apply to monitors and administrators; just because a user is a monitor or administrator does not give them full access to exchanges, queues and bindings through either AMQP or the management plugin.
All users can only list objects within a particular virtual host if they have any permissions for that virtual host.
web 管理台
# 安装管理台
rabbitmq-plugins enable rabbitmq_management
然后 http://localhost:15672 即可访问。
日志记录
rabbitmq-plugins enable rabbitmq_tracing # 启用消息追踪插件,disable 禁用
rabbitmqctl trace_on # 启用消息追踪 trace_off 即为关闭
背后使用的是 Firehose Tracer。https://www.rabbitmq.com/firehose.html
需拥有 administrator 权限,然后在管理台 Admin/Tracing 界面上新增一个 trace 即可。
推荐教程
强烈推荐: http://www.rabbitmq.com/getstarted.html, https://www.rabbitmq.com/tutorials/amqp-concepts.html 概念讲解。
使用场景
实际场景下的 RabbitMQ 使用相关整理。
延迟队列
- 通过消息过期后进入死信交换器,再由交换器转发到延迟消费队列,实现延迟功能;
- 使用
rabbitmq-delayed-message-exchange插件实现延迟功能。